In this part of vCenter deployment series, I will demonstrate the deployment topologies of vCenter server 6.7 so vCenter server 6.7 has two deployment topologies we can either do vCenter with an embedded PSC or vCenter with an external PSC.
In addition, review the steps required to deploy and configure the new vCenter Server Appliance 6.7 with vCenter Embedded PSC, and External PSC and explain how to configure vCenter HA since this feature is still new for the age of vCenter it’s only started with VC 6.5, and PSC load balancing using:
Netscaler Load Balancer.
F5 BIG-IP Load Balancer.
My goal here is to break down vCenter Server 6.7 High Availability (HA) into multiple sections and keep it simple as we agreed.
I will start with an overview of vCenter topologies, vCenter (HA), PSC (LB), and then I will go directly into deployment process.
vCenter 6.7 Topologies
Let’s discuss the features of both types:
Enhanced link mode
So one feature we have is enhanced link mode an enhanced link mode is where we have one or more
vCenter servers visible through a single pane of glass through our vSphere client in vSphere 6.7 both the vCenter with an embedded PSC and vCenter with an external PSC can support enhanced link mode.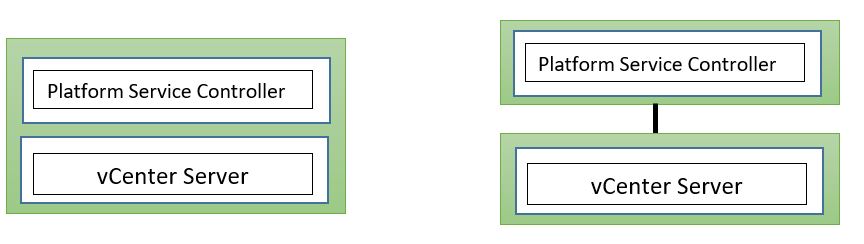
So for example in vCenter with an embedded PSC we can now join an additional embedded vCenter node replicating with the first node to achieve enhanced link mode as shown below.
And similarly, vCenter with an external PSC the same can be true so we can deploy an additional PSC join it to the existing SSO domain and add in more vCenter servers so we can achieve single pane of glass.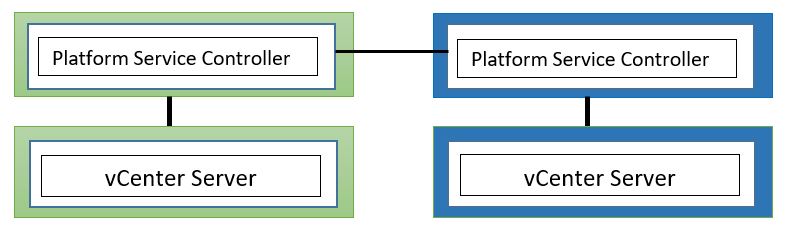
vCenter HA
vCenter HA launched with vSphere 6.5 provides high availability of your vCenter server instance and with vSphere 6.7 vCenter HA will be available in both topology modes even if you’re running vCenter server with an embedded PSC in enhanced link mode so we can enable vCenter HA for both the embedded instances similarly would be vCenter with an external PSC.
When we’re running vCenter with an external PSC it’s important to note that we’re only protecting part of the vCenter layer when we’re using an external PSC, so for that to protect the PSC layer we still have PSC with a load balancer.
vCenter AT Scale
The last thing we’ll explain is vCenter AT Scale so generally, both typologies can support up to fifteen vCenter nodes.
vCenter Server with an Embedded Platform Services Controller
After deploying vCenter Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller, we can reconfigure our topology and switch to vCenter Appliance with an external Platform Services Controller.
This is a one-way process after that we cannot switch back to vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller, but we can repoint the vCenter Server instance only to an external Platform Services Controller that is configured to replicate the infrastructure data within the same domain.
The embedded PSC deployment model does not support Enhanced Linked Mode (ELM); also does not support PSC replication.
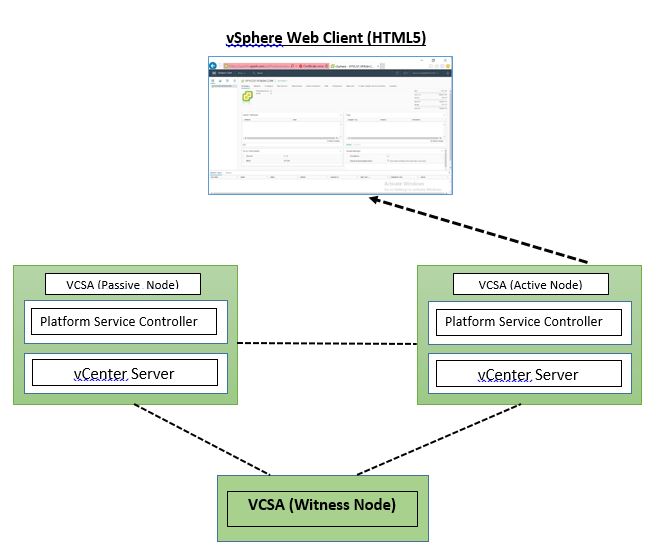
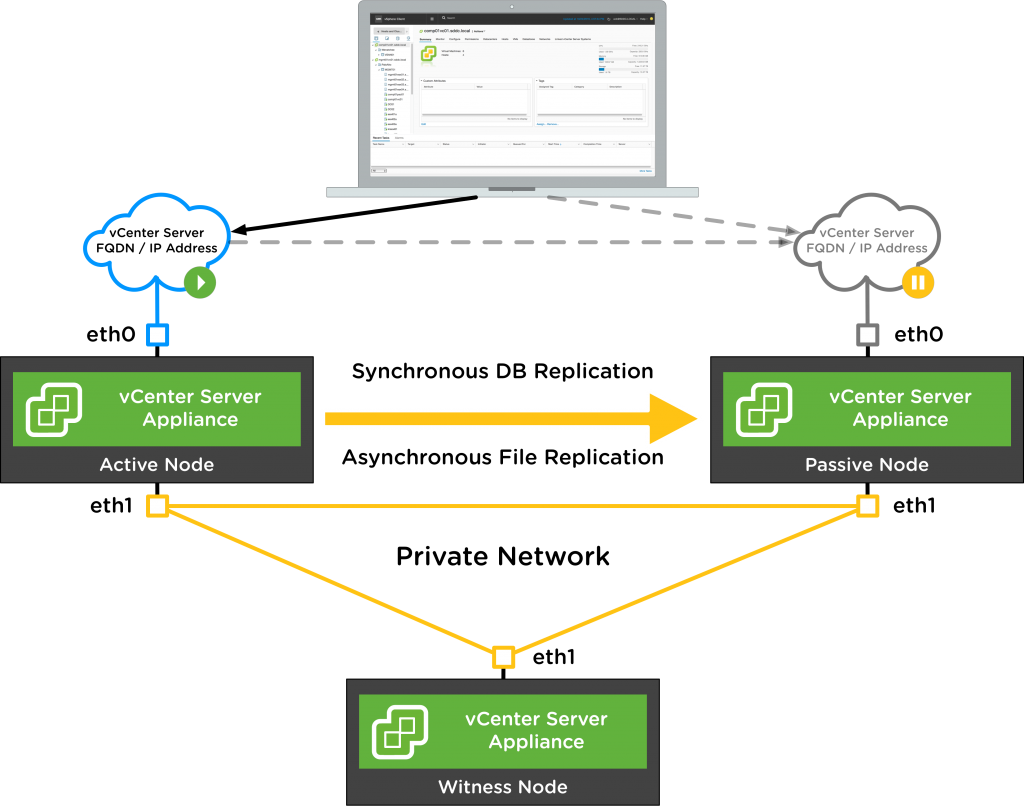
vCenter Appliance in HA mode only contains three appliances deployed after configured HA they are as follows Active, Passive and Witness nodes.
All three will communicate with each other on the vCenter HA network.
vCenter Server with an External Platform Services Controller
If we are going with external platform topology, we must use a load balancer.
In my scenario, I’m going to deploy two PSCs. Once complete the deployment and configuration of PSCs then we should implement vCenter Server Appliance to use the PSC VIP (Virtual IP) provided by the load balancer.
Once the vCenter Server deployment completed, we can use one of the two vCenter HA workflows scenarios to enable vCenter HA.
In my lab, I’m going to deploy everything using the VCSA appliance, at the end I will have six VMs:
- Two external PSCs.
- Three virtual appliances in my vCenter HA configuration: (Active, Passive and Witness nodes)
- One virtual appliance for the load balancer.
First of all, let’s explain a few key features of the vCenter High Availability.
Replication Types:
There are two types of replication between the active and passive nodes.
The first type is native PostgreSQL “synchronous” replication for the DB.
The second type is a separate “asynchronous” replication process used for external data (data not in the DB).
vCenter HA Workflows
It is important to note that both workflows result in the same vCenter HA functionality. We recommend based on VMware recommendation that you use the basic workflow if possible.
Walkthrough for vCenter 6.5 HA, since walkthrough of vCenter 6.7 is not released yet.
The Basic walkthrough is available here.
The Advanced walkthrough is available here.
Lastly, I’d like to mention the very important part of the vCenter 6.7 which is
Thanks.
QUICK LINKS
VCENTER 6.7 DEPLOYMENT &TOPOLOGY – OVERVIEW (PART 1)
VCENTER 6.7 DEPLOYMENT – EMBEDDED PSC (PART 2)
VCENTER 6.7 DEPLOYMENT – EXTERNAL PSC SINGLE NODES (PART 3.1)
VCENTER 6.7 DEPLOYMENT – EXTERNAL PSC SINGLE NODES (PART 3.2)
VCENTER 6.7 DEPLOYMENT – EXTERNAL PSC WITH F5 BIG-IP LOAD BALANCER (PART 4.1)
VCENTER 6.7 DEPLOYMENT – EXTERNAL PSC WITH F5 BIG-IP LOAD BALANCER (PART 4.2)